
The rate avoids collecting actual manufacturing overhead costs as part of the closing period. Cost accountants want to be able to estimate and allocate overhead costs like rent, utilities, and property taxes to the production processes that use these expenses indirectly. Since they can’t just arbitrarily calculate these costs, they must use a rate. Direct labor standard rate, machine hours standard rate, and direct labor hours standard rate are some methods of factory overhead absorption.
FAQs on calculating overhead rate
Tracking any differences between applied and actual overhead also allows companies to improve future overhead estimates. Now management can estimate how much overhead will be required for upcoming work or even competitive bids. For instance, assume the company is bidding on a job that will most likely take $5,000 of labor costs.
Ask Any Financial Question
After going to its terms and conditions of the bidding, it stated the bid would be based on the overhead rate percentage. Therefore, the one with the lower shall be awarded quick ratio formula with examples pros and cons the auction winner since this project would involve more overheads. Hence, this predetermined overhead rate of 66.47 shall be applied to the pricing of the new product VXM.
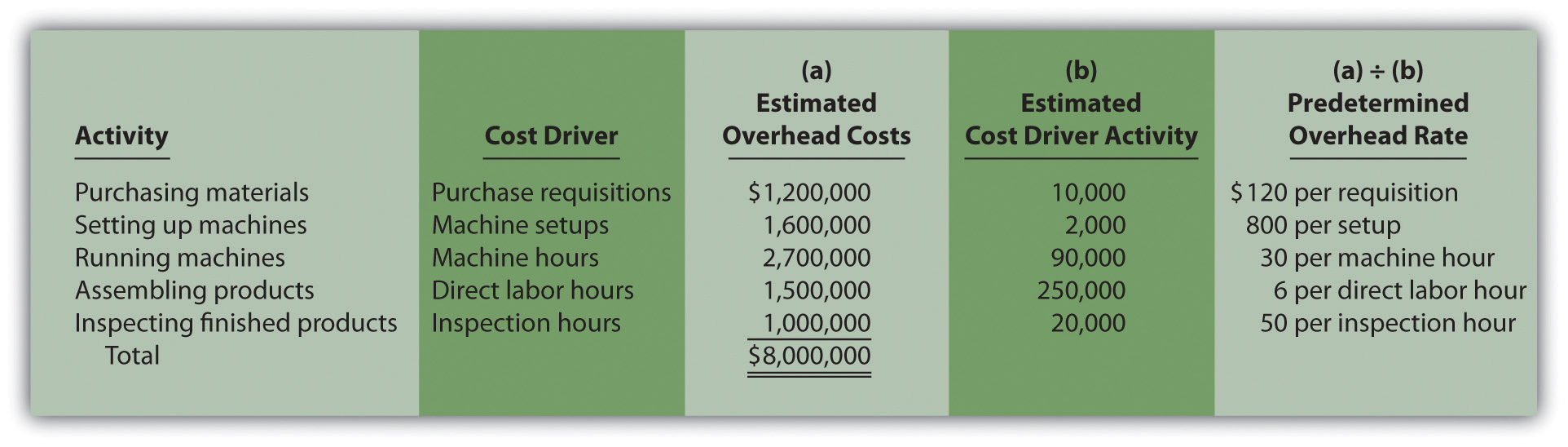
Step 1: Estimate Manufacturing Overhead Costs
As you’ve learned, understanding the cost needed to manufacture a product is critical to making many management decisions (Figure 6.2). Knowing the total and component costs of the product is necessary for price setting and for measuring the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization. Remember that product costs consist of direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Also, if the rates determined are nowhere close to being accurate, the decisions based on those rates will be inaccurate, too. After reviewing the product cost and consulting with the marketing department, the sales prices were set. The sales price, cost of each product, and resulting gross profit are shown in Figure 6.6.
Simplify Any Calculation With Sourcetable
This will help you price your services correctly and increase your profits. If you want to simplify this process, consider using business software like MyOverhead. COGS (Cost of Goods Sold) includes direct costs related to producing products, while overhead includes indirect costs necessary to run the business. It’s a simple step where budgeted/estimated cost is divided with the level of activity calculated in the third stage.
So, the cost of a product in one period may not reflect the cost in another period—for instance, the cost of freezing fish increases in the summer and lowers in the winter. Detailed cost analysis helps to estimate the cost of overheads with accuracy. Further, customized input from different departments can be obtained to enhance the accuracy of the budget. It is necessary for operations but does not directly link to creating a product.
- The activity base (also known as the allocation base or activity driver) in the formula for predetermined overhead rate is often direct labor costs, direct labor hours, or machine hours.
- After going to its terms and conditions of the bidding, it stated the bid would be based on the overhead rate percentage.
- Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
- Understanding these formulas allows businesses to budget for overhead, set predetermined rates, analyze variances, and adjust rates accordingly.
- The predetermined overhead rate is crucial for accurate cost accounting and efficient management of production costs.
This example helps to illustrate the predetermined overhead rate calculation. Two companies, ABC company, and XYZ company are competing to get a massive order that will make them much recognized in the market. This project is going to be lucrative for both companies but after going over the terms and conditions of the bidding, it is stated that the bid would be based on the overhead rate. This means that since the project would involve more overheads, the company with the lower overhead rate shall be awarded the auction winner. Hence, you can apply this predetermined overhead rate of 66.47 to the pricing of the new product X.
So, a more precise practice of overhead absorption has been developed that requires different and relevant bases of apportionment. Businesses normally face fluctuation in product demand due to seasonal variations. Fixed overheads are expected to increase/decrease per unit in line with the seasonal variations.
However, the use of multiple predetermined overhead rates also increases the amount of required accounting labor. The formula for the predetermined overhead rate is purely based on estimates. Hence, the overhead incurred in the actual production process will differ from this estimate. The period selected tends to be one year, and you can use direct labor costs, hours, machine hours or prime cost as the allocation base.
Larger organizations employ different allocation bases for determining the predetermined overhead rate in each production department. These overhead costs involve the manufacturing of a product such as facility utilities, facility maintenance, equipment, supplies, and labor costs. Whereas, the activity base used for the predetermined overhead rate calculation is usually machine hours, direct labor hours, or direct labor costs.