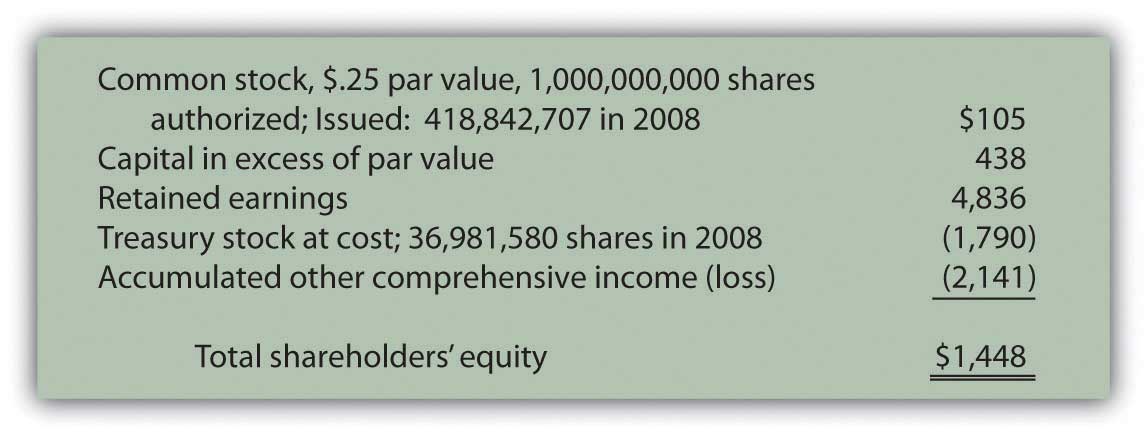
As a result, when companies liquidate or go through a bankruptcy restructuring, common stockholders generally receive nothing, and their shares become worthless. Growth stocks belong to companies expected to experience increasing earnings, which raises their share value. Meanwhile, value stocks are priced lower relative to their fundamentals and often pay dividends, unlike growth stocks. On the other hand, if you’re willing to take on more risk for the chance of bigger returns down the road, common stock is probably more suitable. With common stock, you’re banking on the company growing over time, and you’ll get the added bonus of voting rights on major decisions.
- Instead, when a company offers stock, it confers ownership of a portion of the business to the buyer.
- For investors, common stock enables them to invest in securities that appreciate without significant effort on their part.Common stock dividends can also become an important source of income.
- But before we show an example of an entry of common stock in a balance sheet which is usually done in a shareholders equity, let’s define what is shareholders equity.
- The number of shares outstanding and the total amount of common stock provide important information about the voting rights of shareholders.
- The call price of preferred stock is the amount paid to buy out preferred stockholders.
What should I look for on a business’s balance sheet?
Common stock is part of the equity section because it represents money that shareholders have put into the company. On a company’s balance sheet, common stock is recorded in the “stockholders’ equity” section. This is where investors can determine the book value, or net worth, of their shares, which is equal to the company’s assets minus its liabilities. Some companies choose to distribute some of the profits on their balance sheet to common stockholders in the form of dividends, and each common stockholder is entitled to a proportional share.
Do you own a business?
The calculation of common stock provides additional information about the company’s capital structure and how much money has been invested by shareholders. Additional paid-in capital is also referred to as paid-in capital in excess of par on the balance sheet. The additional paid-in capital is the amount of cash received from the sale of stock shares in excess of the par or stated value of the shares. For example, assume a company issues 100 shares with a stated value of $10 per share, and investors purchase all 100 shares at $15 per share. The company’s additional paid-in capital is $5 per share multiplied by 100 shares.
Calculate Shareholders’ Equity
Let’s explore more about common stock and how it fits into the big picture of a company’s finances. By issuing securities or reducing ownership stakes, the money was obtained. On the other hand, the transaction’s credit impact is reflected in the equity balance.

For example, if a company declares a dividend of $10 million and there are 20 million shareholders, investors will receive $0.50 for each common share they own. Should a company not have enough money to pay all stockholders dividends, preferred stockholders have priority over common stockholders and get paid first. For holders of cumulative preferred stock, any skipped dividend payments accumulate as “dividends in arrears” and must be paid before dividends are issued to common stockholders.
Is common stock an asset on a balance sheet?
Throughout this captivating journey, we will unravel the steps involved in calculating common stock, uncovering the significance of stock issuances, par value, and additional paid-in capital. Together, we will dive into the intricate tapestry of corporate finance, empowering you to see beyond the numbers and grasp the true essence of a company’s financial foundation. The issue and exact figure of dividends for common stock varies and is dependent on company performance. Although the balance sheet is an invaluable piece of information for investors and analysts, there are some drawbacks. For this reason, a balance alone may not paint the full picture of a company’s financial health. Treasury shares continue to count as issued shares, but they are not considered to be outstanding and are thus not included in dividends or the calculation of earnings per share (EPS).
Equity represents the residual interest in the company’s assets after liabilities are deducted. Noncurrent liabilities are items owed over several years, such as business loans, a car loan, or a lease. If a company issues bonds, they will have to pay back the purchaser of the bonds at a later time. Those bonds are thus listed as liabilities on the company’s balance sheet. To ensure the balance sheet is balanced, it will be necessary to compare total assets against total liabilities plus equity. To do this, you’ll need to add liabilities and shareholders’ equity together.
We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. Balance sheets should also be compared with those of other businesses in the same industry since different industries have unique approaches to financing. With Taxfyle, how to get a business loan in 6 simple steps your firm can access licensed CPAs and EAs who can prepare and review tax returns for your clients. Increase your desired income on your desired schedule by using Taxfyle’s platform to pick up tax filing, consultation, and bookkeeping jobs. Taxes are incredibly complex, so we may not have been able to answer your question in the article.
It can also use cash to purchase additional assets used for the business. In the U.S., assets are listed on a balance sheet with the most liquid items (i.e., those that are easiest to sell) listed first and longer-term assets listed lower. When paired with cash flow statements and income statements, balance sheets can help provide a complete picture of your organization’s finances for a specific period. By determining the financial status of your organization, essential partners have an informative blueprint of your company’s potential and profitability. As noted earlier, common stock represents fractional ownership in a company. Each slice represents a share owned by investors, called common stockholders.
Larger U.S.-based stocks are traded on a public exchange, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or Nasdaq. As of mid-2024, the Nasadaq had some 3,377 listings but the NYSE the largest in the world by market cap. Smaller companies that can’t meet the listing requirements of these major exchanges are considered unlisted and their stocks are traded over the counter.